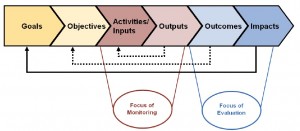
Monitoring and evaluation is closely related to planning. Monitoring is an ongoing activity that focuses on progress in terms of realization of activities and depletion of budget. Monitoring tracks mainly the use of inputs (activities) and outputs, but in some degree also tracks (intermediate) outcomes.
In contrast, evaluation takes place at specific moments, and permits an assessment of a program’s progress over a longer period of time. Evaluation tracks changes and focuses more on the outcome and impact level.
This is illustrated by the following graphic, which shows the link of the chain of inputs, outputs, outcomes and impacts with the planning cycle18:
Output measurement shows the realization of activities. Outcome measurement shows in what degree direct objectives and anticipated results are realized. And impact assessment shows the degree in which the overall objective or goal of the program is realized.
Without defining clear and measurable goals, objectives and activities at the design stage of PPDs, M&E becomes an impossible endeavor. This requires the development of measurable indicators: Specific, Measurable, Achievable/Agreed upon, Relevant/Realistic, Time-bound (SMART) that permit objective verification at a reasonable cost.
At the same time more qualitative indicators also need to be developed, particularly for the outcome and impact level: Subjective, Participatory, Interpreted and communicated, Compared/Cross-checked, Empowering, Diversity/Desegregation (SPICED). These SPICED qualitative indicators address more subjective aspects in M&E.
In this chapter we suggest the use of a combination of standard indicators and customized indicators. This is to:
- provide an objective basis for assessing performance of different PPD processes;
- provide a solid foundation for management decisions; and
- facilitate learning within PPDs and between different PPDs and organizations involved in implementing these PPDs.
This chapter presents an outline of a possible M&E framework that can be used for measuring of different aspects of PPD processes. The focus of the chapter is mainly on evaluation of process, outcome and impact of PPDs. But several components, instruments and indicators can also be used for monitoring, with a focus more on outputs and short-term process developments.
The structure of the chapter is as follows:
- Section 2 presents a three-step approach for task managers who need to develop a comprehensive process evaluation and impact measurement exercise for any particular PPD. This section provides step-by-step guidelines to practitioners for conducting M&E activities, from drafting a project brief to conducting interviews and writing final recommendations.
- Section 3 contains a short description of major approaches and instruments for reliable data collection on process and impact of PPD processes. These approaches and instruments are generally applicable in the evaluation exercise, but the selection of specific instruments will depend on specific aspects of the PDD. These are described in the following sections.
- Section 4 sets out a framework and indicators for the evaluation of operational process and
development of PPDs, and presents some specific suggestions for the use of instruments for
data-collection. - Section 5 presents a framework for evaluation of political economy reform results of PPDs. The framework provides a methodology to assess the degree of impact of a PPD on a standardized set of reform process steps.
- Section 6 presents a general methodology for evaluating the economic impact of PPD. In
conjunction with standardized indicators such as the Doing Business indicators, which can permit comparison and benchmarking of economic results of different PPDs, practitioners will need to customize this model to their own needs and develop indicators related to specific
project objectives. - Section 7 contains practical guidelines for using and customizing the three frameworks for
evaluation of PPDs in different contexts.
See the annexes for standard form M&E instruments that are ready to be used customized.